Office #: 212.221.6121
Cell #: 929.317.8181
Memo Available

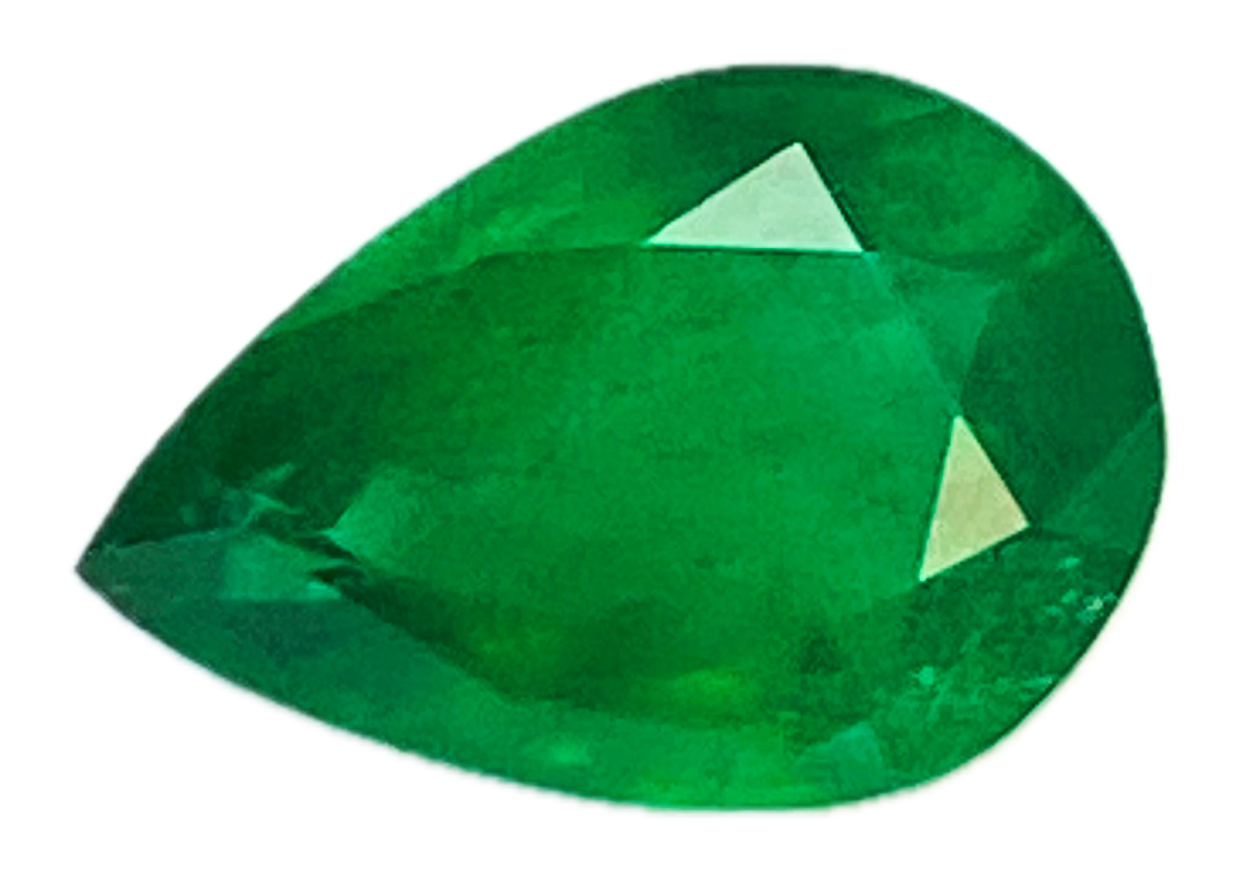
Emerald
Emerald is the rich green to bluish-green variety of the mineral beryl, part of the beryllium aluminum silicate family whose chemical formula is Be₃Al₂(SiO₃)₆ (one of the same species that includes aquamarine) and is colored by trace amounts of chromium and sometimes vanadium embedded in its crystal lattice during formation deep within the Earth’s crust. The vivid green color, the most important factor in determining quality, arises because these trace elements absorb certain wavelengths of light, allowing the characteristic green hues to dominate the spectrum that reaches your eye. Emerald’s crystalline structure is hexagonal, and even fine-quality stones often contain natural internal features known as inclusions or “jardin” (French for garden), which are accepted as typical for this gem and influence both its appearance and value.
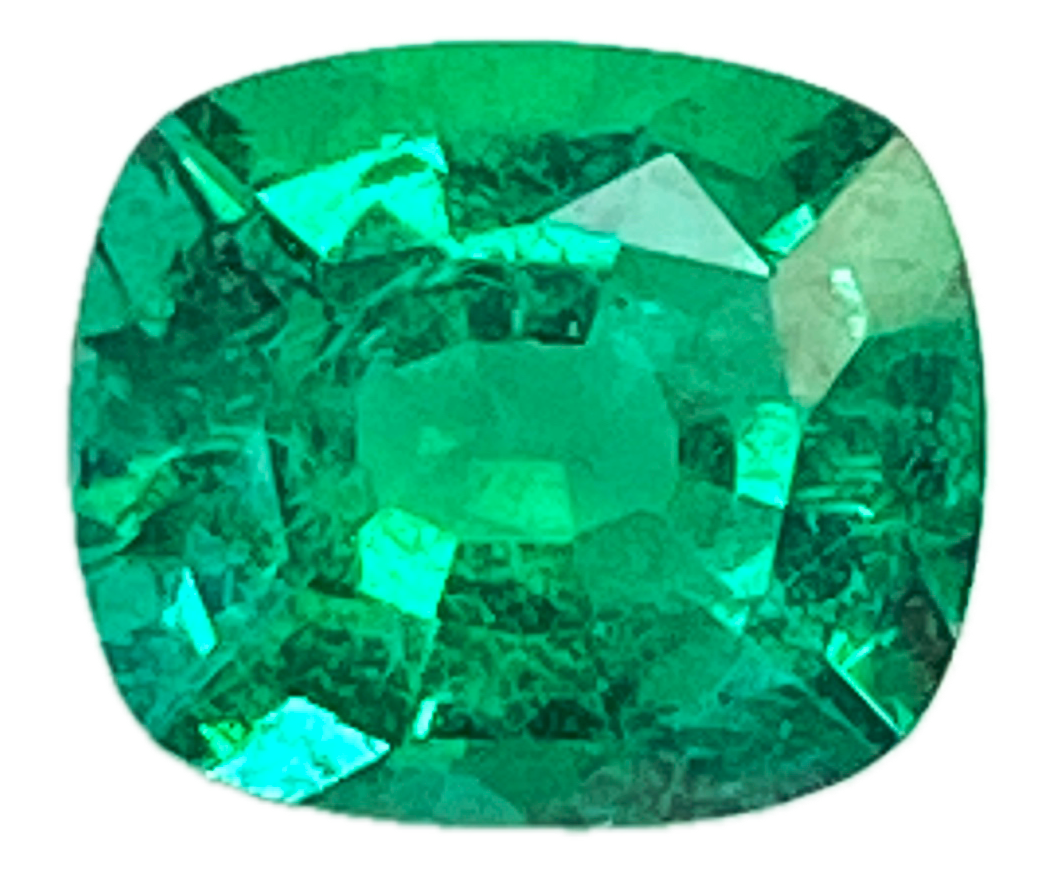

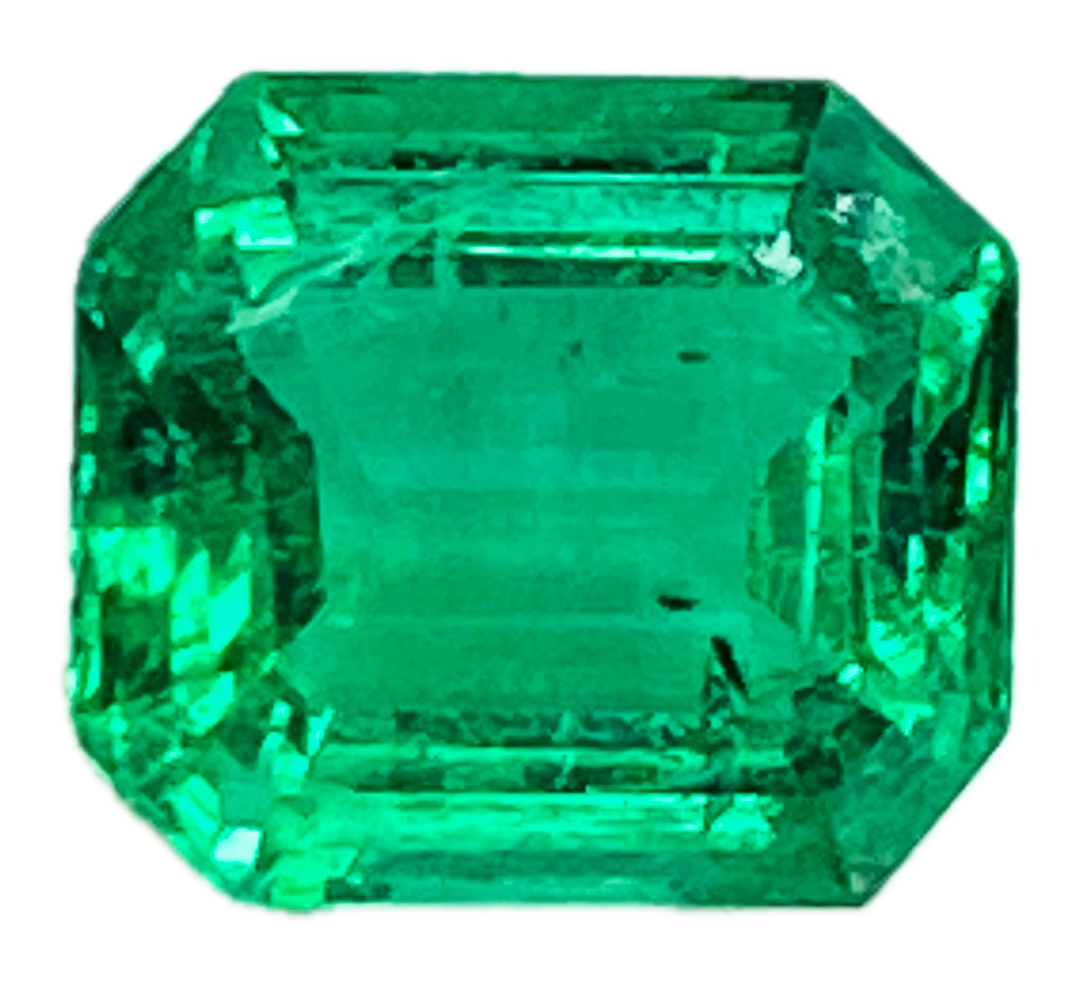
From a gemological perspective, emerald quality is evaluated using the traditional four factors: color, clarity, cut, and carat weight, with color being the most critical. The finest emeralds display a strong, vivid green with good saturation and an even distribution of color across the stone. Unlike diamonds, emerald clarity is judged with greater tolerance, as natural inclusions are common and expected; in fact, these internal features can help confirm natural origin. Emerald is relatively hard ranking about 7.5 to 8 on the Mohs scale. Many emeralds undergo clarity-enhancement treatments, such as the use of oils or resins, to improve transparency, a practice that should always be disclosed and considered when evaluating value and care.





